Amazon Studios, in case you haven’t heard of it, is Amazon’s fairly recent foray into the areas we generally think of as “movies” and “television,” even though much of what we watch these days may not be on movie theater or television screens. I just uploaded a script to Amazon Studios myself. Will it vanish in the noise of thousands of other projects, or will it actually get some attention, possibly even be developed into a feature film?
Before we look at my own project, let’s take a look at Amazon Studios as a whole.
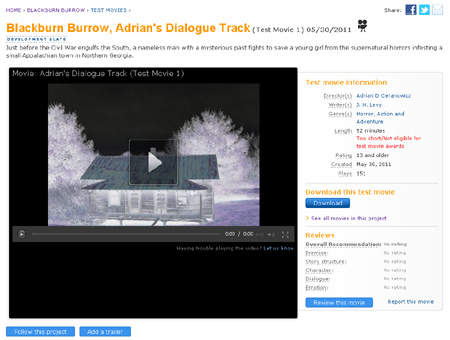
What’s so unusual about Amazon Studios? Well, one of the main things is that they crowdsource content. Writers upload scripts, filmmakers make test movies and trailers from popular uploaded content, and everyone can go around and pick out the projects they like most from the field of contenders. Amazon pays tens or in some cases hundreds of thousands of dollars to develop projects people upload, but most of the projects, of course, go nowhere and earn nothing.
This is not too different from the Kindle Store, where authors can upload books, but most of these books sell few or no copies, while a small number do spectacularly well.
Amazon Studios Will Succeed
I’ll go out on a limb right now and predict that Amazon Studios will make successful films and series that people will watch. Why am I confident of this? Three reasons: crowdsourced content, customer comprehension, and ideal distribution channels.
Crowdsourced content
Crowdsourcing, the process of having a large group of people choose from a field of options, is pretty much ideal (says me) for coming up with movies and video series, because a successfully crowdsourced project means a lot of people like it, and because the single key ingredient for success in a movie or series is that a lot of people like it. Successful crowdsourced products are ones that people talk about, are interested in, and will go out of their way to get to. If the crowd gets interested in a project and that picks it out of the slush, then it stands to reason there’s a very good chance that the larger crowd, which is to say a national or international audience, will also be interested in it and pick it out of other options to actually see, paying money somewhere along the way for the privilege.
Of course it’s true that the crowd that’s doing the picking might not have quite the same preferences as the larger potential audience, or that there might be things that would make a project attractive to project-choosers that wouldn’t make it as attractive to actual audiences, but I suspect these and other limitations are pretty minor, all things considered. I don’t believe that crowdsourced projects are necessarily better than non-crowdsourced ones, or that they should get wider exposure, but I do believe they will tend to be successful.
In my next post, I’ll talk about the other two reasons I believe Amazon will come out on top, the unique advantages they have as a business when it comes to making series and movies.